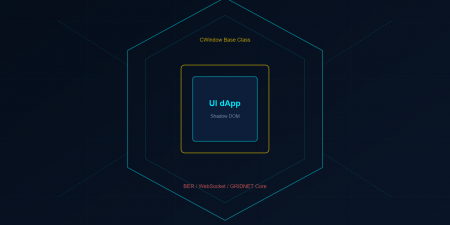
I. What CVMContext Is — And Why It Matters
Every revolution needs a bridge between worlds. The steam engine needed the drive shaft. The internet needed the browser. And GRIDNET OS — the world’s first fully decentralized operating system — needs CVMContext.
CVMContext (defined in /lib/VMContext.js) is the singular JavaScript singleton that connects your UI dApp, running inside a Shadow DOM in the user’s browser, to the entire decentralized stack beneath: the blockchain state machine, the decentralized filesystem, cryptographic identity, WebRTC swarms, consensus tasks, and more. It is not merely an API wrapper. It is the beating heart of every GRIDNET OS application — the central nervous system through which all signals flow.
If you are a web developer building on GRIDNET OS, this is the document you need. Every method. Every event. Every pattern. From first connection to final commit.
The architecture is deceptively simple. Your dApp is standard HTML, CSS, and JavaScript — skills you already have. CVMContext bridges that familiar world to the decentralized one. It communicates with GRIDNET Core full-nodes over WebSocket, serializing commands through the VM Meta Data Protocol (BER-encoded ASN.1) and the DFS Protocol for filesystem operations. The result is that your JavaScript code can navigate directories, read files, send value, deploy contracts, and subscribe to blockchain events — all through a clean, event-driven API.
// The most important line in any GRIDNET OS dApp const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
That single call returns the global singleton. There is only ever one CVMContext — it manages the WebSocket connection, the session key negotiation, the filesystem abstraction, the swarm manager, the channels manager, the keychain, and all event dispatch. Everything flows through it.
II. Connection Lifecycle — From Boot to Ready
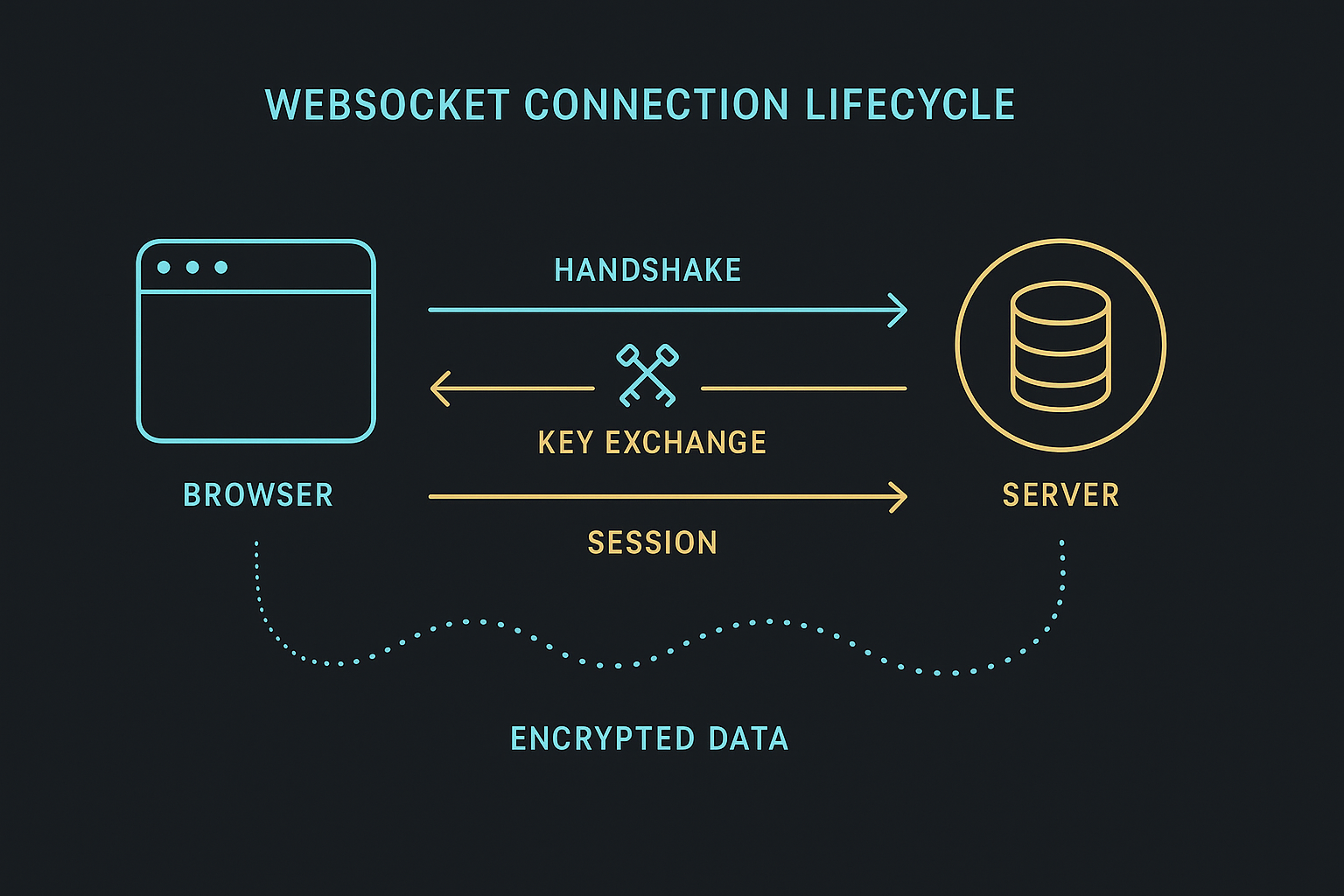
When GRIDNET OS boots in the browser, the bootloader instantiates CVMContext with one or more full-node URIs. What follows is a carefully orchestrated dance of connection, cryptography, and state synchronization.
Phase 1: WebSocket Connection
The CVMContext constructor stores the provided node URIs and starts an internal controller thread (a JavaScript interval at ~2000ms) that manages state transitions. When the context enters the active state, it selects a node URI — either the “closest” one (based on a time-seeded hash heuristic) for the first connection, or a random one for reconnections — and opens a WebSocket.
// The bootloader does this internally: const ctx = new CVMContext(['wss://node1.gridnet.org:26039', 'wss://node2.gridnet.org:26039']); ctx.initialize();
Phase 2: Hello Handshake & Key Exchange
Once the WebSocket opens, CVMContext automatically sends a Hello Request containing a CSessionDescription with the browser’s ephemeral X25519 public key and a random challenge. The full-node responds with its own CSessionDescription. Through ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman), both parties derive a shared session key used for all subsequent communication via ChaCha20-Poly1305 AEAD encryption.
Phase 3: System Thread Spawning
After the session key is established, the full-node spawns a System Thread — a dedicated decentralized processing thread for this connection. The thread ID is communicated back to CVMContext, which stores it. From this point, all GridScript commands execute within this thread’s context.
Connection States
The connection progresses through states defined by eConnectionState:
// Monitor connection state changes
CVMContext.getInstance().addConnectionStatusChangedListener(function(state) {
switch(state) {
case eConnectionState.disconnected:
console.log('Disconnected from GRIDNET Core');
break;
case eConnectionState.connecting:
console.log('Connecting...');
break;
case eConnectionState.connected:
console.log('Connected and ready!');
break;
case eConnectionState.aboutToShutDown:
console.log('Connection weakening (keepalive timeout approaching)');
break;
}
}, this.mID);
CVMContext handles reconnection autonomously. If the connection drops, the controller thread detects it and initiates a new connection to a randomly selected node. For keychain-based logins, the user session persists across reconnections — only QR-based sessions require re-authentication.
VM States
The virtual machine on the full-node also transitions through states tracked by eVMState:
// All eVMState values (from /lib/enums.js):
// eVMState.initializing = 0 — VM is booting up
// eVMState.ready = 1 — VM is ready for commands
// eVMState.aboutToShutDown = 2 — VM is about to shut down
// eVMState.disabled = 3 — VM thread is disabled / unavailable
// eVMState.limitReached = 4 — Resource limit reached
// eVMState.errored = 5 — VM encountered an error
// eVMState.synced = 6 — VM has been synchronized
// eVMState.newPerspectiveAvailable = 7 — New blockchain perspective available
CVMContext.getInstance().addVMStateChangedListener(function(arg) {
// arg.state contains the eVMState value
// arg.extended — if true, additional fields are available:
// arg.vmFlags, arg.vmID, arg.terminalID, arg.conversationID
// arg.threadID — the thread this state applies to
switch(arg.state) {
case eVMState.initializing:
console.log('VM is initializing...');
break;
case eVMState.ready:
console.log('VM is ready — you can now execute commands');
break;
case eVMState.aboutToShutDown:
console.log('VM is about to shut down');
break;
case eVMState.disabled:
console.log('VM thread has been disabled');
break;
case eVMState.limitReached:
console.log('Resource limit reached');
break;
case eVMState.errored:
console.log('VM encountered an error');
break;
case eVMState.synced:
console.log('VM synchronized');
break;
case eVMState.newPerspectiveAvailable:
console.log('New perspective available — refresh state');
break;
}
}, this.mID);
III. Navigation API — cd, ls, pwd, and Domain Resolution
GRIDNET OS organizes all data into State Domains — analogous to user accounts or home directories — stored in Merkle Patricia Tries on the blockchain. Navigation within this filesystem feels intentionally familiar: it uses the same commands as Linux/DOS shells.
The filesystem is accessed through CVMContext.getInstance().getFileSystem, which returns the CFileSystem singleton. All filesystem operations ultimately compile to GridScript commands sent to the full-node.
Changing Directory: cd
const fs = CVMContext.getInstance().getFileSystem;
// Navigate to a state domain (like a user's home directory)
fs.doCD('/alice.gridnet', true, false, false, threadID);
// Navigate to a subdirectory
fs.doCD('documents', true, false, false, threadID);
// Navigate to root
fs.doCD('/', true, false, false, threadID);
The doCD(path, updatePWD, isAbsolute, silent, threadID) method sends a cd GridScript command to the full-node. The path can be absolute (starting with /) or relative. Each State Domain is a top-level directory under /.
Listing Directory Contents: ls
// List current directory
const reqID = fs.doLS(threadID);
// Listen for the result
CVMContext.getInstance().addNewDFSMsgListener(function(dfsMsg) {
// DFS message contains VM Meta Data with directory listing
// Parse entries from the response
}, this.mID);
Listing State Domains: csds
// List all state domains on the blockchain (like listing all user accounts)
// Executed as raw GridScript
CVMContext.getInstance().processGridScript('csds', threadID, processHandle);
Processing GridScript Commands Directly
For navigation and other operations, you can execute any GridScript command through the processGridScript() method:
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
// Full signature:
// processGridScript(cmd, threadID, processHandle, mode, reqID)
// cmd — GridScript command string (default: "")
// threadID — Decentralized thread ID (default: system thread)
// processHandle — Calling CWindow/process (REQUIRED for user-mode)
// mode — eVMMetaCodeExecutionMode (default: RAW)
// reqID — Request ID (default: 0, auto-generated)
// User-mode method (requires a valid process handle)
ctx.processGridScript('cd /alice.gridnet', threadID, myProcessHandle);
ctx.processGridScript('ls', threadID, myProcessHandle);
ctx.processGridScript('pwd', threadID, myProcessHandle);
// With explicit mode (e.g., for terminal-style output)
ctx.processGridScript('ls', threadID, myProcessHandle, eVMMetaCodeExecutionMode.GUITerminal);
Important: processGridScript() is a user-mode method that requires a valid process handle. Anonymous calls will be rejected. This is a security feature — every operation on the decentralized state machine must be attributable to a registered process. For kernel-mode usage (system processes), use processGridScriptKM() which accepts additional parameters including register and promiseInfo for async promise integration. There is also processGridScriptA() which returns a Promise for async/await usage.
IV. File Operations — Full CRUD on the Decentralized Filesystem
The decentralized filesystem supports complete CRUD operations. Each operation maps to a GridScript codeword that the full-node executes against the Merkle Patricia Trie state.
touch — Create an Empty File
// Create a new empty file
ctx.processGridScript('touch myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
write — Write Data to a File
// Write content to a file
ctx.processGridScript('write myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
// Note: content is provided through the DFS protocol's data fields
For file uploads, the FileManager dApp uses the DFS (Decentralized File System) protocol directly:
const fs = CVMContext.getInstance().getFileSystem; // The DFS protocol handles file content through specialized messages // Files can be stored as eternal (permanent) or voted (crowd-funded) storage fs.doCommit(false, threadID); // Commit changes to blockchain
cat — Read File Contents
// Read a file's contents
ctx.processGridScript('cat myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
// Result arrives via GridScript result listener
ctx.addNewGridScriptResultListener(function(result) {
if (result.reqID === myReqID) {
// result.data contains the file content
// result.types contains data type information
console.log('File content:', result.data);
}
}, this.mID);
mkdir — Create a Directory
ctx.processGridScript('mkdir documents', threadID, processHandle);
rm — Remove a File or Directory
ctx.processGridScript('rm myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
head / tail — Read Portions of Files
ctx.processGridScript('head myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
ctx.processGridScript('tail myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
Access Control: chown, setfacl, getfacl
// Change ownership of a file (base58-encoded address)
ctx.processGridScript('chown <base58address> myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
// Set access control list
ctx.processGridScript('setfacl <base58address> myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
// Get current ACL
ctx.processGridScript('getfacl myfile.txt', threadID, processHandle);
The DFS Commit Cycle
All filesystem modifications are transactional. Changes are staged locally and then committed to the blockchain through the DFS protocol. The commit cycle follows this pattern:
const fs = CVMContext.getInstance().getFileSystem;
// 1. Make changes (cd, mkdir, touch, write, rm...)
// 2. Synchronize
fs.doSync();
// 3. Commit changes to blockchain
fs.doCommit(false, threadID);
// 4. Listen for commit result
CVMContext.getInstance().addVMCommitStateChangedListener(function(state) {
switch(state) {
case eCommitState.prePending:
console.log('Commit lock acquired locally');
break;
case eCommitState.pending:
console.log('Full-node confirmed commit is pending');
break;
case eCommitState.success:
console.log('Commit successful! Changes are on the blockchain.');
break;
case eCommitState.aborted:
console.log('Commit was aborted');
break;
}
}, this.mID);
V. Transaction API — BT/CT, Sending Value, Deploying Contracts
GRIDNET OS uses a transaction model that will feel instantly familiar to any database developer. BT (Begin Transaction) opens a transaction context, and CT (Commit Transaction) finalizes it. Between them, you can send value, deploy smart contracts, and modify blockchain state. This maps directly to SQL’s BEGIN/COMMIT paradigm.
Sending Value (GNC Transfer)
GRIDNET OS supports two transaction modes:
1. Remote Mode (Decentralized Threads API) — Commands are sent as GridScript to the full-node for compilation and execution:
// Remote transaction: full-node compiles and executes const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance(); // The Wallet dApp constructs the GridScript command sequence: let cmd = ''; cmd += 'BT '; // Begin Transaction cmd += 'send ' + amount + ' ' + recipientAddress; // Transfer value cmd += ' CT'; // Commit Transaction ctx.processGridScript(cmd, threadID, processHandle, eVMMetaCodeExecutionMode.RAW); // Authentication happens via QR code or local keychain signing // The full-node sends a QRIntentAuth request that CVMContext handles
2. Local Mode (Trustless Browser Compilation) — The transaction bytecode is compiled locally using GridScriptCompiler and sent pre-compiled:
import { GridScriptCompiler } from '/lib/GridScriptCompiler.js';
import { CTransaction } from '/lib/Transaction.js';
// Compile GridScript locally
const compiler = new GridScriptCompiler();
const script = 'send ' + amount + ' ' + recipientAddress;
const result = await compiler.compile(script);
if (result.success) {
// Create and sign the transaction locally
const tx = new CTransaction();
tx.setBytecode(result.bytecode);
// ... set other transaction fields ...
// Submit pre-compiled transaction
const result = await ctx.submitPreCompiledTransactionA(
tx.getPackedData(),
processHandle, // process handle (required)
threadID, // thread ID (optional)
30000 // timeout in ms
);
}
The Commit Lock Mechanism
Before any commit, your dApp must acquire the commit lock. This prevents multiple applications from attempting simultaneous commits:
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
// 1. Try to acquire the commit lock
if (ctx.tryLockCommit(processHandle)) {
// Lock acquired — proceed with commit
// 2. Execute the commit
ctx.commit(processHandle, false, 'system');
// 3. The Magic Button UI changes to "committing" state
// 4. Full-node sends commitPending → commitSuccess/commitAborted
} else {
console.log('Another application is currently committing');
}
The lock has a timeout (mCommitLockTime, default 60 seconds). If the full-node doesn’t confirm within the timeout, CVMContext automatically retries up to 3 times with exponential backoff, then breaks the lock and sends an abort notification.
The submitPreCompiledTransactionA() Method
/**
* Submits a pre-compiled transaction to the network (user-mode, async)
* @param {Uint8Array|ArrayBuffer} txData - BER-encoded transaction bytecode
* @param {Object} processHandle - Calling process (CWindow instance, required)
* @param {ArrayBuffer} [threadID=new ArrayBuffer()] - Thread to execute on (default: system thread)
* @param {number} [timeoutMS=30000] - Timeout in milliseconds
* @returns {Promise} - Resolves with result on success
*/
async submitPreCompiledTransactionA(txData, processHandle, threadID = new ArrayBuffer(), timeoutMS = 30000)
VI. Identity & Authentication

Authentication on GRIDNET OS is cryptographic, not password-based. Your identity is your key pair. CVMContext provides two authentication pathways:
QR Code Authentication
The traditional flow: a QR code is displayed containing the connection’s conversation ID, the full-node’s address, and a random challenge. The user scans it with the GRIDNET Token mobile app, which signs the challenge with their private key and sends the signature back through the full-node.
// Trigger QR login
ctx.requestQRLogon();
// Listen for login
ctx.addUserLogonListener(function(sessionDesc) {
console.log('User logged in:', ctx.getUserID);
}, this.mID);
Local Keychain Authentication (Headless)
The newer, browser-only flow. Users can store encrypted keychains locally (protected by a master password). On login, CVMContext decrypts the keychain and uses it to sign authentication challenges without any mobile device:
// Request login — automatically detects available keychains
await ctx.requestLoginChoice();
// Or directly request keychain login
await ctx.requestKeychainLogin();
// Check login status
if (ctx.isLoggedIn) {
console.log('Logged in as:', ctx.getUserID);
console.log('Keychain login:', ctx.mIsKeychainLogin);
}
Identity Properties
// Get current user ID (State Domain name / address) ctx.getUserID // → "alice.gridnet" or "Anonymous4521" // Get full State Domain ID ctx.getUserFullID // → full state domain identifier // Check if logged in ctx.isLoggedIn // → true/false // Get user session description (contains pubkey, address, etc.) ctx.getUserSessionDescription // → CSessionDescription object // Get key chain manager for programmatic key operations ctx.getKeyChainManager // → CKeyChainManager instance
Session Management
// Logout await ctx.logout(); // Switch identity (keychain logins only) await ctx.switchIdentity(); // Lock screen await ctx.lockScreen();
VII. GridScript Compilation — The GridScriptCompiler
The GridScriptCompiler is a pure JavaScript implementation that compiles GridScript source code into bytecode compatible with GRIDNET Core’s C++ VM. This enables local, trustless transaction compilation — your browser can construct valid blockchain transactions without relying on the full-node for compilation.
import { GridScriptCompiler } from '/lib/GridScriptCompiler.js';
const compiler = new GridScriptCompiler();
// Compile a simple value transfer
const result = await compiler.compile('send 100 recipientAddress');
if (result.success) {
console.log('Bytecode:', result.bytecode); // Uint8Array
console.log('No errors');
} else {
console.log('Compilation errors:', result.errors);
}
Bytecode Format
The compiler generates V2 bytecode by default:
V2: [VERSION_BYTE][32_BYTE_HASH][OPCODES...] - VERSION_BYTE: 194 (0xC2) for V2 - 32_BYTE_HASH: SHA-256 keyword image hash chain - OPCODES: Encoded codeword instructions
The keyword hash chain provides integrity verification: H₀ = SHA256("GRIDSCRIPT_V2_KEYWORD_IMAGE"), then Hₙ = SHA256(Hₙ₋₁ || keyword) for each compiled keyword. This ensures the bytecode hasn’t been tampered with.
Opcode Encoding
- ID ≤ 127: Single byte [ID] - ID > 127: Two bytes [HIGH_BYTE | 0x80][LOW_BYTE] (little-endian with bit 7 set)
Key Codewords for dApp Developers
| Codeword | Opcode | Description |
|---|---|---|
cd |
162 | Change directory |
ls |
174 | List directory contents |
mkdir |
165 | Create directory |
touch |
262 | Create empty file |
rm |
263 | Remove file/directory |
write |
233 | Write to file |
cat |
104 | Read file contents |
send |
195 | Transfer value (2 inline params) |
balance |
198 | Query balance |
chown |
225 | Change ownership (base58) |
setfacl |
223 | Set access control (base58) |
getfacl |
227 | Get access control |
call |
152 | Call smart contract |
echo |
157 | Output text |
whoami |
235 | Current identity |
info |
199 | Domain information |
Encoding Utilities: CTools
The full CTools class is exported from /lib/tools.js and provides a comprehensive set of utilities — encoding, formatting, BigInt conversion, logging, GNC value formatting, and much more. This is the CTools that CVMContext itself uses internally.
Important distinction: /lib/GridScriptCompiler.js also exports a class named CTools, but it is a stripped-down, environment-agnostic version containing only crypto and encoding utilities (SHA-256, Base58Check, Base64Check). This lightweight version exists so the compiler can run in both browser and Node.js environments without DOM dependencies. If you need the full toolkit (GNC formatting, path parsing, byte vector comparison, logging, etc.), import from /lib/tools.js.
// Full CTools — used by CVMContext and most dApps
import { CTools } from '/lib/tools.js';
const tools = CTools.getInstance();
// Base58Check encode/decode (for addresses)
const encoded = await tools.encodeBase58Check(binaryData);
const decoded = await tools.decodeBase58Check(encodedString);
// Base64Check encode/decode
const b64 = await tools.encodeBase64Check(binaryData);
// SHA-256
const hash = await tools.sha256(data);
// String ↔ Bytes
const bytes = tools.stringToBytes('hello');
const str = tools.bytesToString(bytes);
// GNC value formatting
const formatted = tools.formatGNCValue(valueInAttoGNC, 5); // → "1.5 GNC"
// --- Stripped-down CTools for compiler/Node.js use ---
// import { CTools } from '/lib/GridScriptCompiler.js';
// Only has: encodeBase58Check, decodeBase58Check, encodeBase64Check,
// decodeBase64Check, sha256, stringToBytes, bytesToString
VIII. The Event System — Subscriptions and State Notifications
CVMContext’s architecture is fundamentally event-driven. Rather than polling for state changes, you register callback functions that fire when specific events occur. Every listener method returns a unique listener ID that can be used for later removal.
Complete Event Listener Registry
| Method | Event |
|---|---|
addConnectionStatusChangedListener(cb, appID) |
WebSocket connection state changes |
addVMStateChangedListener(cb, appID) |
Decentralized VM state transitions |
addVMCommitStateChangedListener(cb, appID) |
Commit operation state changes |
addContextStateChangedListener(cb, appID) |
CVMContext internal state changes |
addNewNetMsgListener(cb, appID) |
Raw network messages (CNetMsg) |
addNewDFSMsgListener(cb, appID) |
DFS protocol messages |
addVMMetaDataListener(cb, appID) |
VM Meta Data protocol messages |
addNewGridScriptResultListener(cb, appID) |
GridScript execution results |
addNewTerminalDataListener(cb, appID) |
Terminal I/O data |
addNewAppDataListener(cb, appID) |
Application-specific data |
addUserLogonListener(cb, appID) |
User login events |
addUserActionRequestListener(cb, appID) |
User interaction requests (QR, password) |
addUserNotificationsListener(cb, appID) |
System notifications |
addNewKeyBlockListener(cb, appID) |
New key blocks appended to chain |
addNewDataBlockListener(cb, appID) |
New data blocks appended to chain |
addNewConsensusActionListener(cb, appID) |
Consensus task updates |
addSessionKeyAvailableListener(cb, appID) |
Session key established |
addOperationStatusListener(cb, appID) |
Operation status notifications |
addNewSwarmSDPMsgListener(cb, appID) |
WebRTC SDP signaling messages |
addDFSRequestCompletedListener(cb, appID) |
DFS request completion |
addNewSearchResultsListener(cb, appID) |
Blockchain search results |
addNewBlockDetailsListener(cb, appID) |
Block detail responses |
addNewDomainDetailsListener(cb, appID) |
Domain detail responses |
addNewTransactionDetailsListener(cb, appID) |
Transaction detail responses |
addBlockchainStatsListener(cb, appID) |
Blockchain statistics |
Pattern: Register → Listen → Unregister
class MyDApp extends CWindow {
constructor() {
super(/* ... */);
// Register listeners — store the IDs for cleanup
this.vmListenerID = CVMContext.getInstance()
.addVMStateChangedListener(this.onVMStateChanged.bind(this), this.mID);
this.dfsListenerID = CVMContext.getInstance()
.addNewDFSMsgListener(this.onDFSMessage.bind(this), this.mID);
}
onVMStateChanged(arg) {
if (arg.state === eVMState.ready) {
this.loadData();
}
}
onDFSMessage(dfsMsg) {
// Process filesystem responses
}
// Clean up when window closes
closeWindow() {
CVMContext.getInstance().unregisterEventListenersByAppID(this.mID);
super.closeWindow();
}
}
Critical: Always unregister your listeners when your dApp window closes. Use unregisterEventListenersByAppID(appID) for bulk cleanup, or unregisterEventListenerByID(id) for individual removal.
IX. WebRTC Swarms — Cross-Browser Communication

GRIDNET OS includes a built-in WebRTC Swarms system that enables direct browser-to-browser communication without relying on the full-node for data transfer. The full-node serves only as the signaling server for ICE negotiation.
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
const swarms = ctx.getSwarmsManager; // CSwarmsManager instance
// Join the global swarm
const swarmID = ctx.getMainSwarmID; // 'global'
// Listen for SDP signaling messages
ctx.addNewSwarmSDPMsgListener(function(sdpEntity) {
// Handle WebRTC signaling
// sdpEntity contains offer/answer/ICE candidates
}, this.mID);
// Get ICE server configuration
const iceServers = ctx.ICEServers;
The Messenger dApp demonstrates the full WebRTC pattern: SDP offer/answer exchange through the GRIDNET signaling infrastructure, ICE candidate gathering, and direct peer data channel establishment. This enables real-time messaging, file sharing, and collaborative features between browsers.
X. Blockchain Explorer API
CVMContext provides a comprehensive set of methods for querying blockchain data. Each method comes in two variants: a callback-based version (returns a request ID) and an async/Promise-based version (suffixed with A).
Async API Examples
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
// Get blockchain status
const status = await ctx.getBlockchainStatusA(threadID, processHandle);
// Get recent blocks
const blocks = await ctx.getRecentBlocksA(10, 1, eSortBlocksBy.timestampDesc,
threadID, processHandle);
// Get recent transactions
const txs = await ctx.getRecentTransactionsA(10, 1, false, threadID, processHandle);
// Search the blockchain
const results = await ctx.searchBlockchainA('alice', 10, 1, null,
threadID, processHandle);
// Get domain details
const domain = await ctx.getDomainDetailsA('alice.gridnet', '', false,
threadID, processHandle);
// Get domain transaction history
const history = await ctx.getDomainHistoryA('alice.gridnet', 10, 1,
eSortTransactionsBy.timestampDesc, '', threadID, processHandle);
// Get block details
const block = await ctx.getBlockDetailsA(blockID, true, false, false,
threadID, processHandle);
// Get transaction details
const tx = await ctx.getTransactionDetailsA(txID, threadID, processHandle);
// Get blockchain height
const height = await ctx.getHeightA(false, threadID, processHandle);
const keyHeight = await ctx.getHeightA(true, threadID, processHandle);
// Get USDT price
const price = await ctx.getUSDTPriceA(threadID, processHandle);
// Get market data
const market = await ctx.getMarketDataA(true, true, 1, 50, null,
eSortOrder.ascending, threadID, processHandle);
// Subscribe to real-time updates
await ctx.subscribeToBlockchainUpdatesA(threadID, processHandle);
XI. Advanced Features — Token Pools, State-Less Channels, DFS
Token Pools
GRIDNET OS supports Multi-Dimensional Token Pools — custom tokens that can be deployed on the blockchain. The CStateLessChannelsManager and related classes handle token pool operations:
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance(); const channels = ctx.getChannelsManager; // CStateLessChannelsManager // User's token pools are tracked const pools = ctx.getUserTokenPools; // Token pool operations use GridScript: // regPool — register a token pool // getPool — query pool state // xTT — transfer tokens // poll — poll for updates
State-Less Channels
State-Less Channels provide instant, off-chain payment channels. They work by establishing a cryptographic commitment between parties that can be settled on-chain at any time:
const channels = CVMContext.getInstance().getChannelsManager; // CStateLessChannelsManager handles channel lifecycle // CStateLessChannel represents individual channels // CTransmissionToken represents off-chain payment proofs
Process & Thread Management
// Create a JavaScript thread (runs in browser)
const threadID = ctx.createJSThread(
myFunction, // function to execute
processID, // owning process
1000, // interval in ms
true, // auto-start
false // kernel mode
);
// Stop a thread
ctx.stopJSThread(threadID);
// Create a decentralized thread (runs on full-node)
const reqID = ctx.createThread(threadID, processID);
// Free a decentralized thread
ctx.freeThread(threadID, processID);
// Send data to a thread
ctx.sendDataToThread(threadID, data);
Terminal Integration
// Send a line to the terminal
ctx.sendLine('ls -la\r\n', processID);
// Send a keystroke
ctx.sendKeyStroke(13, processID, threadID); // Enter key
// Send terminal dimensions
ctx.sendTerminalDimensions(24, 80, processID);
XII. Complete CVMContext Method Reference
Core Singleton & Identity
| Method/Property | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
CVMContext.getInstance(...nodeURIs) |
CVMContext | Get or create the singleton instance |
initialize() |
void | Initialize all subsystems (called by bootloader) |
genRequestID() |
number | Generate a unique request ID |
get getUserID |
string | Current user identifier |
set setUserID |
void | Set user identifier |
get getUserFullID |
string | Full state domain identifier |
get isLoggedIn |
boolean | Whether a user session is active |
get getUserSessionDescription |
CSessionDescription | Current user session details |
requestLoginChoice() |
void | Show login method selection dialog |
requestQRLogon() |
void | Show QR code for mobile app login |
requestKeychainLogin() |
Promise | Login via local keychain |
logout() |
Promise | Logout and clear session |
switchIdentity() |
Promise | Switch sub-identity (keychain only) |
lockScreen() |
Promise | Lock screen requiring re-auth |
Connection & State
| Method/Property | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
get getConnectionState |
eConnectionState | Current WebSocket connection state |
get getVMState |
eVMState | Current VM state |
get getState |
eContextState | Context internal state |
get getCommitState |
eCommitState | Current commit operation state |
get getFullNodeIP |
string | Current full-node IP address |
get getCurrentNodeURI |
string | Current WebSocket URI |
get getSessionKey |
ArrayBuffer | Current session encryption key |
get getConversationID |
ArrayBuffer | Local conversation identifier |
get getSystemThreadID |
ArrayBuffer | System decentralized thread ID |
get getIsCommiting |
boolean | Whether a commit is in progress |
forceNode(nodeURI) |
void | Force connection to specific node |
clearForcedNode() |
void | Clear forced node selection |
endConnection() |
void | Terminate current connection |
GridScript Execution
| Method | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
processGridScript(cmd, threadID, processHandle, mode?, reqID?) |
boolean|reqID | Execute GridScript (user-mode, requires process handle). Defaults: mode=RAW, reqID=auto |
processGridScriptA(cmd, threadID, processHandle, mode?, reqID?, timeoutMS?) |
Promise | Execute GridScript (async/Promise-based, user-mode) |
processGridScriptKM(cmd, threadID, processHandle, mode?, reqID?, register?, promiseInfo?) |
number|false | Execute GridScript (kernel-mode, returns reqID) |
submitPreCompiledTransactionA(txData, processHandle, threadID?, timeoutMS?) |
Promise | Submit pre-compiled transaction bytecode (user-mode, async) |
processVMMetaData(generator, processHandle) |
boolean | Send VM Meta Data (user-mode) |
Filesystem & Subsystems
| Property | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
get getFileSystem |
CFileSystem | Decentralized filesystem interface |
get getSwarmsManager |
CSwarmsManager | WebRTC swarms manager |
get getChannelsManager |
CStateLessChannelsManager | State-less channels manager |
get getKeyChainManager |
CKeyChainManager | Local keychain manager |
get getCryptoFactory |
CX25519 | Cryptographic operations (ECDH, signing) |
get getLocalDataStore |
CLocalDataStore | Browser-local storage |
get getWindowManager |
CWindowManager | Window management |
get getPackageManager |
CPackageManager | dApp package management |
get getSettingsManager |
CSettingsManager | Per-user settings |
get getDNS |
CDNS | DNS resolution |
get getMagicButton |
CMagicButton | Magic Button (commit UI control) |
get getMetaParser |
CVMMetaParser | VM Meta Data parser |
get getMetaGenerator |
CVMMetaGenerator | VM Meta Data generator |
Transaction & Commit
| Method | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
tryLockCommit(appHandle, breakLock) |
boolean | Attempt to acquire commit lock |
commit(appHandle, breakLock, threadID) |
boolean | Execute commit operation |
breakCommitLock(wasSuccess) |
void | Release the commit lock |
syncVM(breakCommit, processHandle) |
boolean | Synchronize with VM state (user-mode) |
syncVMKF(breakCommit, processHandle) |
boolean | Synchronize with VM state (kernel-mode) |
scopeSystemThread(scopeCommitTarget, scopeHomeDir) |
boolean | Scope system thread to user’s domain |
set setCommitTarget |
void | Set target network (TestNet/MainNet) |
get getCommitTarget |
eBlockchainMode | Current target network |
get getTotalPendingOutgressTransfer |
BigInt | Total pending outgoing value |
Thread & Process Management
| Method | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
createJSThread(funcPtr, processID, intervalMS, autoRun, isKernelMode) |
number | Create a browser-side JS thread |
stopJSThread(threadID) |
boolean | Stop a JS thread |
createThread(threadID, processID) |
number | Create decentralized thread on full-node |
freeThread(threadID, processID) |
boolean | Free a decentralized thread |
sendDataToThread(threadID, data, netMsgType) |
boolean | Send data to a specific thread |
getThreadByID(id) |
CThread|null | Find thread by ID across all processes |
getNewProcessID() |
number | Generate new user-mode process ID |
getNewThreadID(isKernelMode) |
number | Generate new thread ID |
registerProcessByWinHandle(windowHandle) |
boolean | Register a CWindow as a process |
unregisterProcess(processID) |
boolean | Unregister a process |
getProcessByID(id) |
CProcess | Find process by ID |
getProcessByThreadID(id) |
CProcess|null | Find process owning a thread |
Blockchain Explorer API
| Method | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
getRecentTransactions(size, page, includeMem, ...) |
reqID | Get recent transactions (callback) |
getRecentTransactionsA(size, page, ...) |
Promise<CSearchResults> | Get recent transactions (async) |
getRecentBlocks(size, page, sort, ...) |
reqID | Get recent blocks (callback) |
getRecentBlocksA(size, page, ...) |
Promise | Get recent blocks (async) |
searchBlockchain(query, size, page, flags, ...) |
reqID | Search blockchain (callback) |
searchBlockchainA(query, ...) |
Promise | Search blockchain (async) |
getBlockDetails(blockID, includeTX, ...) |
reqID | Get block details (callback) |
getBlockDetailsA(blockID, ...) |
Promise | Get block details (async) |
getDomainDetails(address, perspective, ...) |
reqID | Get domain details (callback) |
getDomainDetailsA(address, ...) |
Promise | Get domain details (async) |
getDomainHistory(address, size, page, ...) |
reqID | Get domain tx history (callback) |
getDomainHistoryA(address, ...) |
Promise | Get domain tx history (async) |
getTransactionDetails(txID, ...) |
reqID | Get transaction details (callback) |
getTransactionDetailsA(txID, ...) |
Promise | Get transaction details (async) |
getBlockchainStatus(...) |
reqID | Get blockchain status (callback) |
getBlockchainStatusA(...) |
Promise | Get blockchain status (async) |
getHeight(isKeyHeight, ...) |
reqID | Get chain height (callback, cached) |
getHeightA(isKeyHeight, ...) |
Promise<number> | Get chain height (async, cached) |
getUSDTPrice(...) |
reqID | Get USDT price (callback) |
getUSDTPriceA(...) |
Promise | Get USDT price (async) |
getLiveness(...) |
reqID | Get liveness state (callback) |
getLivenessA(...) |
Promise | Get liveness state (async) |
getTransactionDailyStats(days, ...) |
reqID | Get daily tx stats (callback) |
getTransactionDailyStatsA(days, ...) |
Promise | Get daily tx stats (async) |
getNetworkUtilization24h(...) |
reqID | 24h network utilization (callback) |
getNetworkUtilization24hA(...) |
Promise | 24h network utilization (async) |
getBlockSize24h(...) |
reqID | 24h avg block size (callback) |
getBlockSize24hA(...) |
Promise | 24h avg block size (async) |
getBlockRewards24h(...) |
reqID | 24h avg rewards (callback) |
getBlockRewards24hA(...) |
Promise | 24h avg rewards (async) |
getAverageBlockTime24h(...) |
reqID | 24h avg block time (callback) |
getAverageBlockTime24hA(...) |
Promise | 24h avg block time (async) |
getAverageKeyBlockTime24h(...) |
reqID | 24h avg key-block time (callback) |
getAverageKeyBlockTime24hA(...) |
Promise | 24h avg key-block time (async) |
getMiningDifficulty(count, start, end, ...) |
reqID | Mining difficulty stats (callback) |
getMiningDifficultyA(count, ...) |
Promise | Mining difficulty stats (async, cacheable) |
getMarketData(getMarketCap, getBalances, ...) |
reqID | Market data (callback) |
getMarketDataA(getMarketCap, ...) |
Promise | Market data (async) |
subscribeToBlockchainUpdates(...) |
boolean | Subscribe to real-time updates |
subscribeToBlockchainUpdatesA(...) |
Promise<boolean> | Subscribe to updates (async) |
unsubscribeFromBlockchainUpdates(...) |
boolean | Unsubscribe from updates |
unsubscribeFromBlockchainUpdatesA(...) |
Promise<boolean> | Unsubscribe from updates (async) |
Networking & Security
| Method/Property | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
sendNetMsg(msg, breakCommit, UINotifyOnError) |
boolean | Send authenticated/encrypted CNetMsg |
sendDFSMsg(msg, breakCommit) |
boolean | Send DFS protocol message |
notifyMobileToken(status, scope, reqID) |
boolean | Send notification to mobile app via onion routing |
notifyOperationStatus(status, scope, reqID) |
boolean | Notify operation status to peer |
get getKeyPair |
Object | Ephemeral X25519 key pair |
get ICEServers |
Array | WebRTC ICE server configuration |
set setDoSignOutgressMsgs |
void | Enable/disable message signing |
get publicIPAddress |
string | Auto-detected public IP |
UI & Logging
| Method/Property | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
logAppEvent(info, process, entryType, priority) |
void | Log a user-mode application event |
set setLoggingEnabled |
void | Enable/disable logging |
set setLogVMStatus |
void | Enable/disable VM status logging |
set setLogNetPackets |
void | Enable/disable network packet logging |
set setLogVMmeta |
void | Enable/disable VM Meta Data logging |
set setLogTerminalPackets |
void | Enable/disable terminal packet logging |
set setLogAppEvents |
void | Enable/disable app event logging |
addGUITask(task, dispatchNotifications) |
boolean | Add a task to the GUI task queue |
playSound(sound) |
void | Play a system sound |
enterFullscreen() |
void | Enter fullscreen mode |
exitFullscreen() |
void | Exit fullscreen mode |
set setGamingModeEnabled |
void | Toggle performance/gaming mode |
Consensus Tasks
| Method | Returns | Description |
|---|---|---|
addConsensusTask(task, isLocal) |
void | Add a consensus task to the queue |
getConsensusTaskByDescription(desc, subDesc) |
CConsensusTask|null | Find task by description |
get getConsensusTasks |
Array | All pending consensus tasks |
get getConsensusTasksCount |
number | Number of pending tasks |
clearPendngConsensusTasks() |
void | Clear all pending tasks |
XIII. Putting It All Together — A Complete dApp Pattern
Here is the canonical pattern for a GRIDNET OS UI dApp that uses CVMContext:
import { CWindow } from '/lib/window.js';
class MyDApp extends CWindow {
static getPackageID() {
return 'org.example.mydapp';
}
static getIcon() {
return '/images/mydapp-icon.png';
}
constructor(x, y, w, h) {
super(x, y, w, h, myHTMLBody, 'My dApp', MyDApp.getIcon(), false);
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
// 1. Register for events
ctx.addVMStateChangedListener(this.onVMStateChanged.bind(this), this.mID);
ctx.addNewDFSMsgListener(this.onDFSMessage.bind(this), this.mID);
ctx.addNewGridScriptResultListener(this.onGridScriptResult.bind(this), this.mID);
ctx.addConnectionStatusChangedListener(this.onConnectionChanged.bind(this), this.mID);
ctx.addVMCommitStateChangedListener(this.onCommitStateChanged.bind(this), this.mID);
}
onVMStateChanged(arg) {
if (arg.state === eVMState.ready) {
// VM is ready — safe to execute commands
this.loadInitialData();
}
}
onConnectionChanged(state) {
if (state === eConnectionState.disconnected) {
this.showDisconnectedUI();
}
}
async loadInitialData() {
const ctx = CVMContext.getInstance();
if (ctx.getConnectionState !== eConnectionState.connected) {
this.showNotConnectedError();
return;
}
// Navigate to user's home directory
const fs = ctx.getFileSystem;
fs.doCD('/' + ctx.getUserID, true, false, false, this.getThreadID);
fs.doLS(this.getThreadID);
}
onDFSMessage(dfsMsg) {
// Handle filesystem responses
}
onGridScriptResult(result) {
// Handle GridScript execution results
}
onCommitStateChanged(state) {
// Handle commit lifecycle
}
// CRITICAL: Clean up listeners on close
closeWindow() {
CVMContext.getInstance().unregisterEventListenersByAppID(this.mID);
super.closeWindow();
}
}
XIV. Conclusion — The Bridge Is Open
CVMContext is not just an API — it is the philosophical bridge between the familiar world of web development and the uncharted territory of decentralized computing. Through it, every HTML form submission can become a blockchain transaction. Every file save can become an immutable state change. Every chat message can traverse a peer-to-peer mesh without touching a central server.
The design philosophy is clear: meet developers where they are. You don’t need to learn a new language. You don’t need to understand Merkle Patricia Tries. You don’t need to implement cryptographic protocols. CVMContext handles all of that. You write JavaScript. You subscribe to events. You call methods. The decentralized world opens up.
This is Article 4 in our UI dApp Developer Series. With the foundation laid in previous articles on Shadow DOM architecture and the WebUI framework, and with this deep dive into CVMContext, you now possess the knowledge to build production-grade decentralized applications on GRIDNET OS.
The bridge is open. Start building.
— The Wizards of GRIDNET OS